Digital Sharing Economy and Sustainability
Researchers Involved
research areas
timeframe
2017 - 2020
contact
pouri@ifi.uzh.chMotivation
- The current patterns of production and consumption are not sustainable. The increasing trend in natural resource depletion calls for new ways that could significantly change the prevailing
unsustainable consumption practices. - The new practices of the digital sharing economy, along with the rules and regulations that influence them, have implications for patterns of consumption at a large scale.
- There is a lack of a systematic approach for investigating the (positive or negative) sustainability
impacts of the digital sharing economy.
Project Goals
- Establishing a theoretical framework for explaining the existing and anticipating the future forms of digitally enabled sharing systems.
- Designing a conceptual model for structuring the opportunities and risks of the digital sharing economy (DSE) for sustainability.
- Developing a guideline for the sustainability assessment of DSE business models.
Relevant Questions
- How can we precisely describe the spectrum of phenomena usually referred to as ‘sharing economy’ in the context of digitalization, and how can the social practices of digital sharing be characterized?
- What are the causal links between the DSE and sustainable development, and how can we apply and extend existing conceptual models to structure them?
Under what conditions can digital sharing contribute to sustainable patterns of resource consumption
and resource use? - How to model the DSE to create model-based support of the sustainability assessment of its actual and potential instances?
The Digital Sharing Economy (DSE) is:
A class of resource allocation systems based on sharing practices which are coordinated by digital online platforms and performed by individuals, and possibly (non-) commercial entities, with the aim to provide temporary access to durable resources (without transfer of ownership) and/or shared consumption of consumable resources. Digital sharing systems operate in the space between traditional sharing and formal markets and can generate non-monetary or monetary value for their participants.

The Case of Shared Mobility
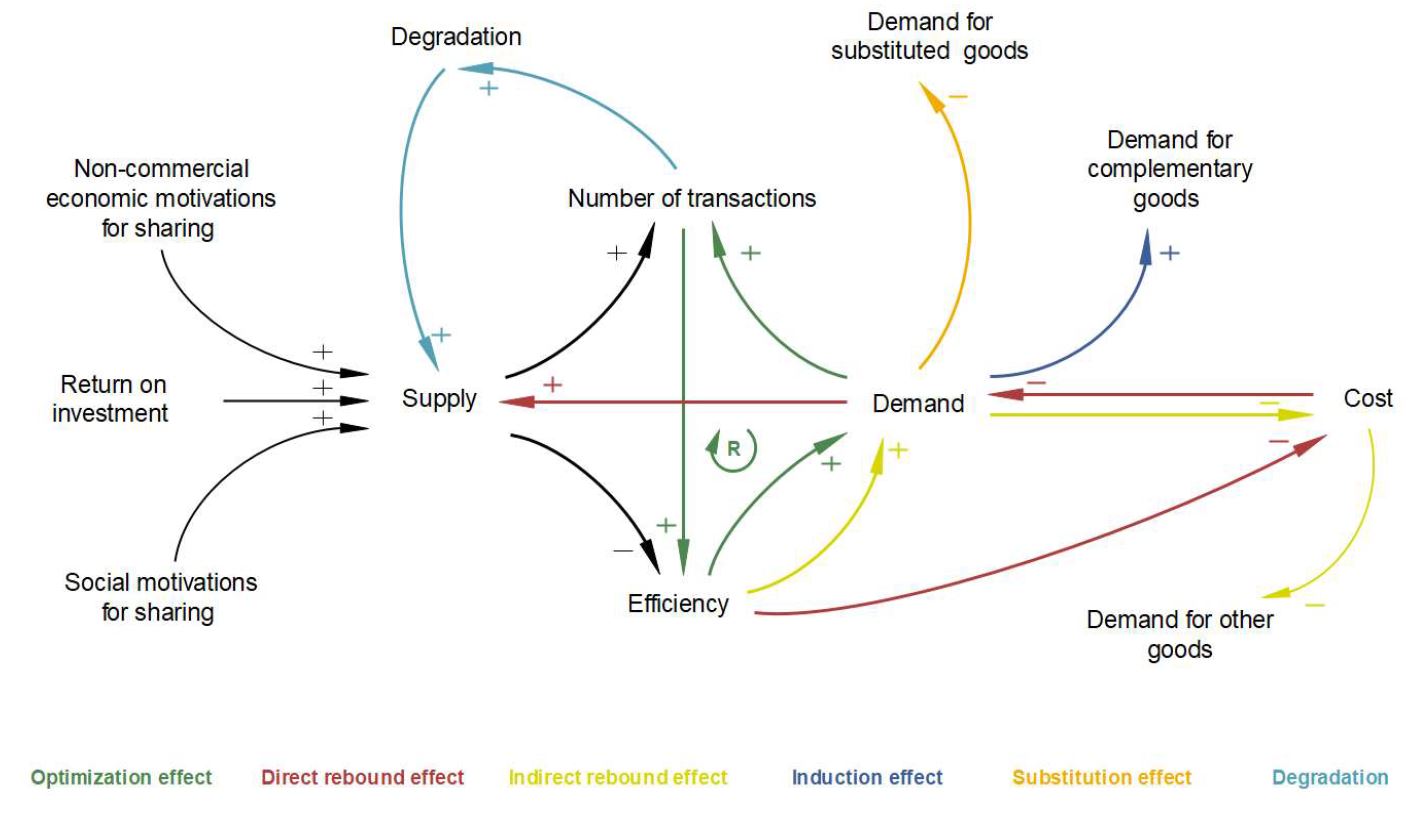
A Causal Model for Explaining the Sustainability Impacts of Consumption in the Digital Sharing Economy:
- Optimization effect
- Induction effect
- Substitution effect
- Direct rebound effect
- Indirect rebound effect
- Faster degradation of vehicles